THERMAL SPACER BLOCK MATERIAL (TSBM)
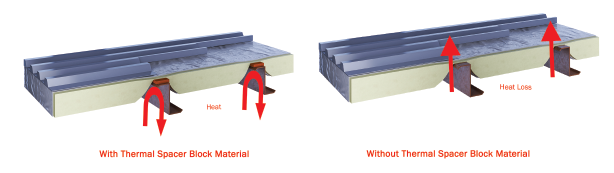
Thermal Spacer Block Material (TSBM) thermal break material reduces heat loss at wall and roof purlin connections. It is used between metal roof or wall panels and the purlins/girts to increase the thermal resistance of walls and roofs in metal buildings.
TSBM material is produced, manufactured and fabricated in the USA and complies with the “Build America, Buy America” act.
The purpose of a thermal break is to reduce the impact of thermal bridging by
reducing conductive heat flow through the building’s thermal envelope. Thermal
breaks also help to keep surface temperatures within the thermal envelope above
the dew point. This eliminates potential condensation risk.
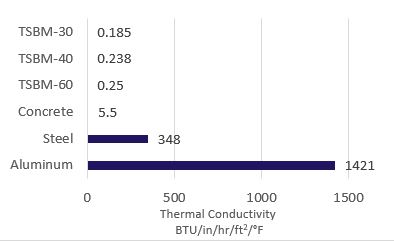
TSBM conducts heat up to 5,500 times less than aluminum, 1,400 times less than
steel, and up to 22 times less than concrete. For any material, conduction is a
function of thickness and temperature difference, so the thickness of a thermal
break material should be carefully considered.
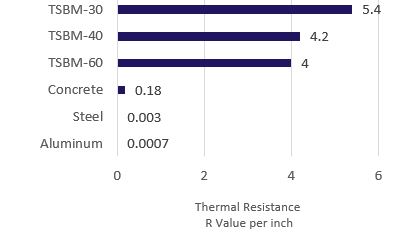
The thermal conductivity of a material is a function of its conductance and is an
important value in determining the rate at which heat flows through that material.
Heat flow is also dependent on area and temperature. To be effective, a thermal
break has to have a much, much lower thermal conductivity than the material it is
“breaking”. Since the conductance of a material is a function of its thickness, both
thickness and area are important in heat flow calculations for a thermal break.
TSBM is available in thickness from 1/2″ to 6″ and is supplied in 8’x4′ sheets or cut to size.
In any connection design using a thermal break, the goal is to find the appropriate
thickness/area combination that helps the wall or roof assembly meet the U value
requirement based on climate zone and energy code.