THERMAL BREAK MATERIAL
(TBM-3)
Window opening thermal break, column base thermal break. Thermal Break Material (TBM-3) conducts heat 2,800 – 5,900 times less than aluminum, 700-1,450 times less than steel and 10-23 times less than concrete. For any material, conduction is a function of thickness and temperature difference. Thickness of a thermal break material should be carefully considered. Armatherm 500 and Fabreeka RF are equal to TBM-3.
This material is manufactured in a range of load capacities for various load conditions within the building envelope. It can be used as a thermal break under columns, roof posts, and dunnage connections providing continuous insulation where thermal bridging normally occurs. It is also an effective thermal break at curtain wall and storefront transitions.
It is used in window rough openings or as a support buck for metal framed window and door installations. This reduces conductive heat loss between the metal frames and steel stud or wood frame openings.
TBM-3 material is produced, manufactured and fabricated in the USA and complies with the “Build America, Buy America” act.

• Supports up to 2,200 psi
• Thermal resistance of R 2 – R 4.2 per inch
• Mildew, mold, rot and moisture resistant
• LBC Red List Free
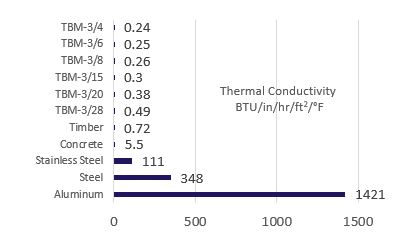
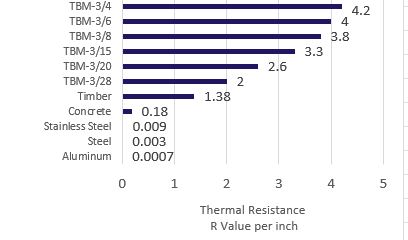
The thermal conductivity of a material is a function of its conductance which helps determine the rate at which heat flows through that material. Heat flow is also dependent on area and temperature.
Conductance is a function of thickness, so to be effective at reducing heat flow through a connection, the thickness of the thermal break is important.
This material is available in thicknesses from 1/2″ to 12″ to accommodate a wide range of connection details. In any connection design, the goal is to use the appropriate thickness/area which helps meet energy code requirements for the wall or roof assembly.

TBM-3/15 thermal break material used in the window rough opening to reduce thermal bridging between the steel studs and the window frame
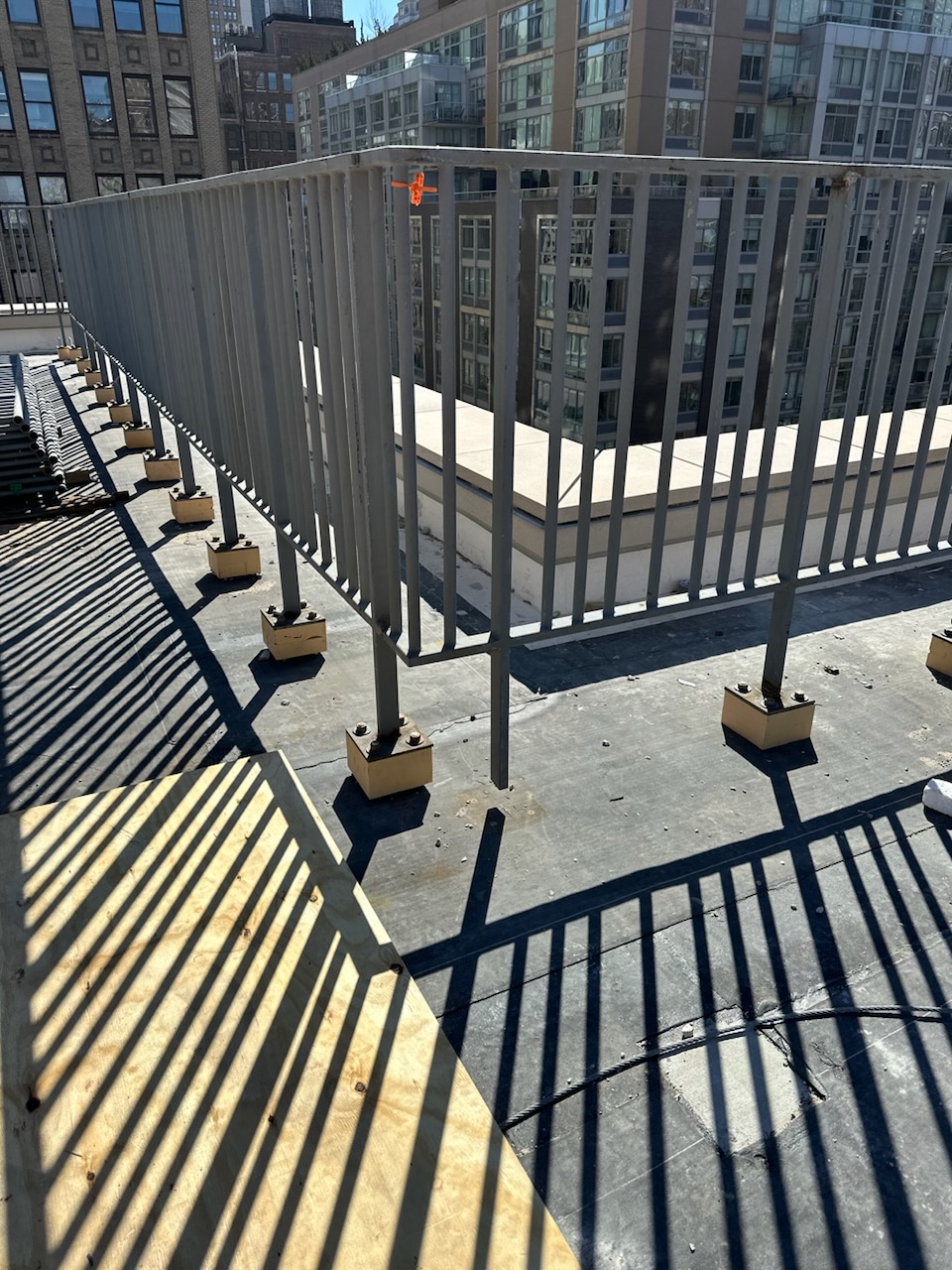

TBM-3 thermal break material supporting railing posts within the exterior roof insulation. This reduces heat loss that would have occurred due to thermal bridging if the posts passed through the insulation uninterrupted.


