Thermal Break Applications
Solutions for Thermal Bridging
It has been established that the heat loss caused by thermal bridging significantly reduces the R value of roofs, walls and foundations. The amount of heat lost depends on the building enclosure design, climate zone and type of thermal bridging detail. Thermal breaks improve the effective R value of wall and roof assemblies and help keep material surface temperatures above the dew point. Thermal bridging occurs at many locations within the building envelope. Below we have given a list of these locations in walls, roofs and foundations.

For each application, thermal bridging can occur at single connection points (think canopy or roof post) or at areas defined by length (think masonry shelf angle or foundation wall). Heat flow at these details is commonly referred to as transmittance – point transmittance or linear transmittance per unit length. Transmittance lowers R value. Even the clear field R value of a wall or roof can be reduced due to thermal bridging at fasteners, Z girts, clips, etc. These heat flow paths (point, linear and clear field) result in lower than expected R values and higher energy consumption.

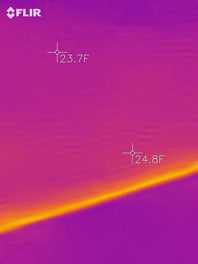
Heat Loss At Foundation Wall Transition
Thermal Bridging Locations in the Building Envelope
Parapet, Roof Edge, Dunnage Support, Wind/Equipment Screen Post, Fall Arrest Anchor
Roof purlins, wall purlins, column bases, wall to foundation
Balconies, Canopies, Sunshades
Steel, concrete, precast,
Clips, brackets, shelf angles, modular panel connections
Anchors, support plates, mullions
Window and Door frame attachments, thresholds, lintels
Wall to Foundation transitions, beam connections
If you have a technical question about any of our structural thermal break products or thermal bridging solutions in general, please contact us to discuss.


